Perspiration is a natural phenomenon essential to our survival. It enables our body to lower its temperature when faced with intense heat or physical exertion. However, for some people, sweating goes beyond the body’s normal cooling needs, creating a state of discomfort and embarrassment. This phenomenon is called hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating.
Perspiration: a natural process in the human body
Perspiration is a vital cooling mechanism. Our sweat glands, integrated into our skin, produce sweat when stimulated by a rise in body temperature, whether due to physical activity, environmental heat or stress. This sweat, once evaporated from the surface of our skin, helps keep our body temperature stable. However, in individuals with hyperhidrosis, this natural perspiration becomes excessive, leading to undesirable physical and emotional consequences.
Hyperhidrosis: when normal perspiration becomes excessive

Hyperhidrosis is a condition that leads to excessive sweating, far beyond what is necessary to regulate body temperature. This condition can affect different areas of the body, such as the hands (palmar hyperhidrosis), feet (plantar hyperhidrosis), armpits (axillary hyperhidrosis) and face (facial hyperhidrosis). The causes of hyperhidrosis are generally linked to overactivity of the sweat glands, controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Diagnosing hyperhidrosis can be a complex process, as perspiration levels vary from person to person. However, if you experience excessive sweating for no obvious reason, or endure unexpected episodes of intense perspiration, you could be suffering from hyperhidrosis. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss treatment options.
Treatments for hyperhidrosis: a range of options available
 The treatment of hyperhidrosis can be as diverse as its manifestations. Various options are available, from topical solutions to surgical interventions, to meet the specific needs of each individual.
The treatment of hyperhidrosis can be as diverse as its manifestations. Various options are available, from topical solutions to surgical interventions, to meet the specific needs of each individual.
For starters, clinical deodorants, or antiperspirants, are often the first line of defense against hyperhidrosis. These products generally contain aluminum salts that help block the sweat glands’ ducts, reducing sweat production. They are mainly used to treat axillary hyperhidrosis, but can also be effective on other areas of the body.
Another non-invasive option is oral medication, such as anticholinergics. These drugs work by blocking communication between nerves and sweat glands, thereby limiting sweat production. However, they can have side effects, such as dry mouth and constipation, and these drugs are not usually the first choice of treatment.
For more severe hyperhidrosis, iontophoresis may be an option. This procedure involves passing a weak electric current through the skin using a medical device. The electric current interferes with the function of the sweat glands, reducing perspiration. Iontophoresis is generally used to treat palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis.
Among the most effective treatment options are botulinum toxin injections. Botulinum toxin acts by blocking the nerve signals that stimulate the sweat glands, thereby reducing sweat production. It is generally used to treat axillary, palmar and plantar hyperhidrosis, and the effects can last several months.
Finally, for the most severe cases of hyperhidrosis, surgery may be considered.
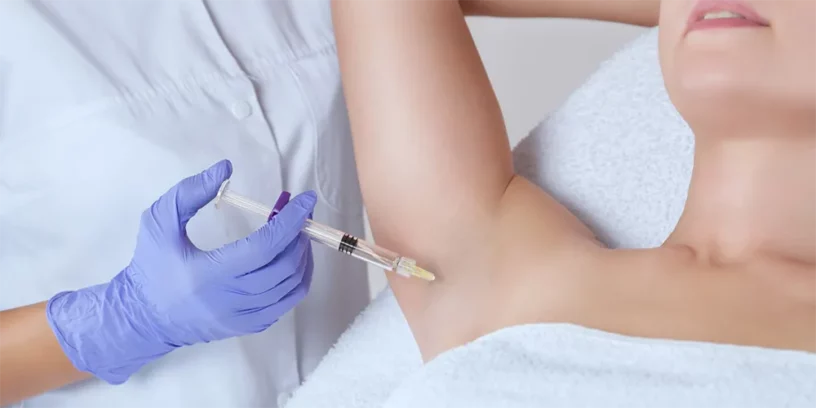
A medical condition that deserves attention and support
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating. It can have a major impact on the quality of life of sufferers. Fortunately, thanks to medical advances, there are a variety of treatments available to help manage this condition.
If you’re concerned about hyperhidrosis, you may want to consider your options. A consultation with a healthcare professional can help assess your symptoms and explore the various treatment options available.

