What is breast augmentation?
Breast augmentation is one of the most common and safest aesthetic procedures. It is a procedure that increases the volume and improves the shape of the breasts, resulting in a more balanced and proportionate figure.
As with any surgical decision, the choice to undergo breast augmentation must be carefully considered. It’s important to understand the process, the different types of implants available, the placement techniques used, the potential results and the risks involved.
Why choose breast augmentation?
This cosmetic surgery procedure is designed to enhance the size and shape of the breasts. One of the main motivations is improved self-esteem. Indeed, many women report increased self-confidence after the procedure. The procedure helps them achieve the breasts they desire, contributing to their general well-being and personal satisfaction.
Breast augmentation can also be used to rebalance body proportions. For women with a wide pelvis or asymmetrical breasts, for example, breast augmentation helps to create a more harmonious silhouette .
Furthermore, following pregnancy or major weight loss, which can cause loss of volume and sagging of the breast skin, breast augmentation can bring a sense of rejuvenation by restoring the previous size of the breasts or even making them fuller. Finally, breast augmentation can help correct breast deformities, offering a more natural breast appearance.
The benefits of breast augmentation
- Improved breast symmetry
- Obtaining fuller breasts
- Cleavage enhancement
- Improved breast projection for a more pronounced contour
- Restore breast volume lost through aging, weight loss or pregnancy
- Access to more clothing choices
- Building self-confidence
- Offer customized results
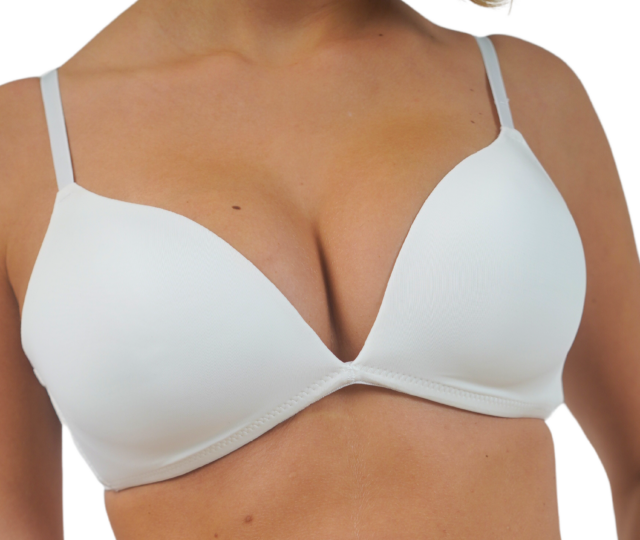

Breast augmentation: some important points
What are the different types of breast implants?
Today, the majority of prostheses are essentially filled with cohesive silicone gel. Historically, one of the most common complications of breast augmentation was the formation of a rigid membrane, called a shell or capsule, around the prosthesis, which could lead to breast deformity and even pain.
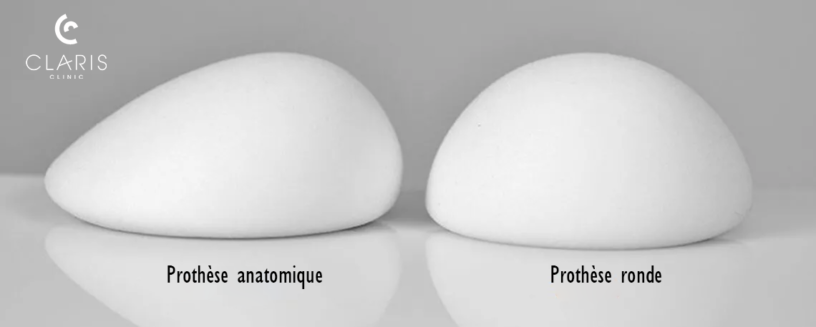
The most common types of prosthesis are :
- The popular round shape gives the breast a full, rounded appearance, accentuating the curvature of the upper part of the breast.
- The anatomical or “teardrop” shape, designed to mimic the natural shape of the breast, offers a more natural appearance.
- The ergonomic shape, which is a round prosthesis that is less dense and less filled, making it possible to give the breast an anatomical shape while avoiding the risk of prosthesis rotation.
The volume of these prostheses generally ranges from 200 to 800 cc, although implants outside this range do exist. Before undergoing breast augmentation, it’s crucial to consult a qualified plastic surgeon to determine the type of implant best suited to your morphology and expectations. The surgeon will examine your breasts, discuss your goals and inform you of the potential risks associated with the operation. During this consultation, you’ll have the opportunity to try on different sizes of external prostheses to defineyour desired volume.
Which implant volume to choose?
Choosing the right volume of breast implants to achieve the desired result can be complex. This choice depends on a number of factors, including your morphology, your figure and your expectations in terms of results. Your aesthetic surgeon will guide you through these considerations to determine together the volume and shape of your prostheses.
The profile of breast implants determines the projection of the breast. There are different implant profiles:
- Low profile: For slight augmentation and medium cleavage.
- Medium profile: For natural augmentation and intermediate cleavage.
- High profile: For an impressive décolleté with breasts projected forward.
- Very high profile: For a very imposing décolleté with significant projection.
The choice of implant volume is also crucial in determining cup augmentation.
Implants range from 125cc to over 1500cc. Depending on the number of cc (cubic centimeters), your breasts will be one or more cup sizes larger. Most women prefer breast implants of no more than 500cc for a natural result.
| Augmentation | Breast implant volume |
| From cup A to cup B | 250 to 300 cc |
| From cup A to cup C | 300 to 350 cc |
| A cup to D cup | 370 to 430 cc |
| B cup to C cup | 250 to 350 cc |
| From B cup to D cup | 350 to 400 cc |
| B cup to DD cup | 400 to 450 cc |
| From cup C to cup D | 300 to 350 cc |
| C cup to DD cup | 370 to 450 cc |
| C cup to E cup | 450 to 550 cc |
| From cup D to cup DD | 300 to 400 cc |
| From cup D to cup E | 450 to 600 cc |
Measure your cup size precisely
The cup size is determined by the difference between the waist circumference and the bust circumference. For an accurate measurement, position the tape measure on the most prominent part of the bust, typically at the nipple. A difference of 12.5 cm is equivalent to an A cup, and each additional 2.5 cm increases the cup size.
What are the possible approaches?
The different types of scars possible for breast augmentation depend on the surgical technique used and your personal preference. The most common types of scars associated with breast augmentation are :
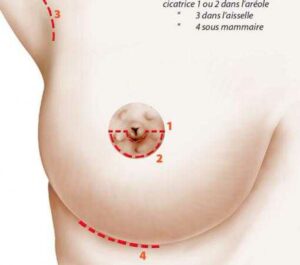
Peri-areolar scar Peri-areolar scar: this scar is located around the areola, and may be more visible if it is not well hidden by the edge of the areola. It also has the disadvantage of having to pass through the mammary gland to insert the implant. In addition, this approach makes it more difficult to fix the lower pole properly, and the prosthesis runs the risk of dropping below the natural fold of the breast after a few years.
Inframammary scar This scar lies under the breast (“submammary fold”) and can be hidden by the lower edge of the bra. It allows good control of the operation and is by far the most frequently used.
Axillary scar This scar is located in the armpit. However, it may require a longer incision, is more visible and can be more problematic or a source of infection. It is virtually no longer used.
Where is the breast implant placed?
Behind the pectoral muscle Behind the pectoral muscle: implants placed behind the pectoral muscle are generally less visible, especially when tissue thickness is insufficient. However, the retropectoral approach can lead to more intense pain during recovery, and is mainly reserved for very thin women with very little breast tissue. In addition, this technique carries a greater risk of upward and/or outward migration of the implants in the longer term, under the effect of muscle contractions. There is also a higher risk of premature implant rupture (before 10 years), as the implants are subject to greater wear and tear, due to muscle contractions and friction on the ribs, whose surface is sometimes highly irregular.
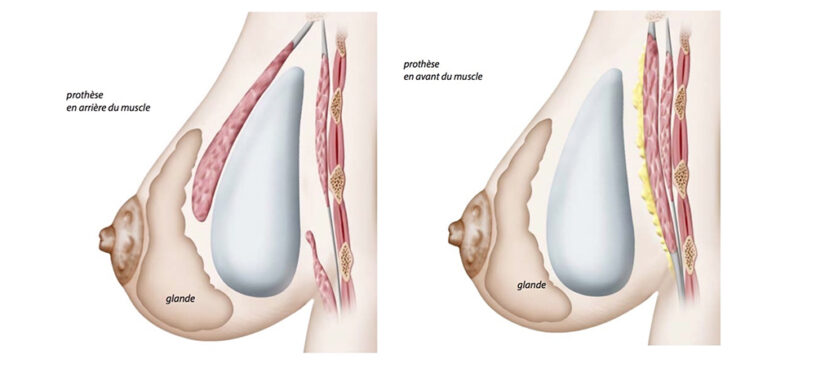
In front of the pectoral muscle In front of the pectoral muscle: the implant is placed above the pectoral muscle. This type of implantation is simpler and can achieve good results when the thickness of the gland is sufficient to camouflage the prosthesis. However, results may vary if the thickness of the gland decreases over the course of the patient’s life (pregnancy, menopause, weight loss).
How long do breast implants last?
Silicone breast implants are generally considered “reliable”, and can last a minimum of 10 to 15 years. However, this may depend on a number of factors, such as the type of implant used, implant quality, general health and post-operative care. It’s important to talk to your surgeon to get a clearer idea of how long your breast implants will last.
It is also important to remember that breast prostheses sometimes need to be replaced over timefor reasons such as leakage, displacement or loss of shape. So you need to keep a close eye on your body and follow up regularly with your surgeon to make sure everything is going well.
As with all women, you should continue to undergo breast cancer screening. If an X-ray examination is prescribed, it is advisable to inform the radiologist of the presence of implants.
Breast augmentation: when is it appropriate?
The decision to undergo breast augmentation surgery is a personal one. Women’s breasts differ in appearance and volume, and in some cases they may wish to correct the shape of their breasts.
This dissatisfaction may be linked to a personal perception of the body, or may, for example, arise following one or more pregnancies. In particular, some women see their breasts change and lose volume after giving birth and breast-feeding their child(ren).
What are the possible complications of breast augmentation?
Potential complications of breast augmentation include:
Hematoma The most frequent complication is hematoma, which can appear within the first 24 hours. The submammary approach has made it possible to reduce the frequency of haematomas. In the event of significant hematoma, the implant should be removed, blood clots evacuated and the source of bleeding investigated before the implant is replaced.
Infection Infection may occur following surgery, leading to pain, fever and breast enlargement.
Capsular contracture Capsular contracture: capsular contracture occurs when the body produces a fibroid envelope around the implant (inflammatory reaction) which can cause it to shrink and become hard.
Scars Scars may be more visible or painful than expected, and may take longer to fade.
Implant rejection Rejection of a breast implant can occur when the body rejects the implant as a foreign body. This complication is extremely rare.
Implant displacement The implant may move or shift from its initial position over time.
Implant rupture Implant rupture: implants can sometimes break or leak, leading to pain and breast enlargement.
How do I choose my breast augmentation surgeon?
There are several factors to consider when choosing a surgeon:
Competence and experience Make sure the surgeon has solid training and experience in cosmetic breast surgery. Ask for photos of previous procedures to get an idea of the surgeon’s skill level.
Certifications Check that the surgeon is certified by the appropriate medical societies. In Belgium, recognized surgeons are members of the Royal Belgian Society of Plastic Surgery(https://www.rbsps.org/fr/accueil.html).
Communication Communication: Make sure you feel comfortable talking openly with your surgeon about your expectations and concerns. Good communication with your surgeon is important for a satisfying and confident result.
Rates Make sure you understand the costs associated with the operation. In fact, it’s essential to ask for details of the fees that will be included in the final price, such as the surgeon’s fees, anesthesia, hospitalization and equipment costs.
Is this a routine procedure?
Breast augmentation is a common and safe surgical procedure for improving breast size, shape and symmetry. Our clinic offers personalized solutions for every patient, using the latest techniques and technologies to ensure natural, long-lasting results. This is an important and personal decision, which is why we take the time to understand your needs and expectations to offer you the most suitable treatment. Contact us to find out more about breast augmentation and to schedule a consultation with our team of plastic surgery specialists.
Your other questions
- There are no contraindications to breastfeeding after breast augmentation. Only the peri-areolar incision may reduce the ability to breastfeed. Talk to your surgeon!
- It’s perfectly possible to have a mammogram with implants if you’ve had a breast augmentation. However, please inform the technician and radiologist before the examination.
- Claris Clinic works only with the best implant brands, offering the highest standards of safety and quality. The incidence of breast cancer in women with implants is extremely low.
Your journey in 3 steps
- Consultation
- Surgery
- Post-operative follow-up

At a glance
60-90 min.
On an outpatient basis
After 1 day
6 weeks
1 to 2 weeks
1 week
1 to 2 week(s)
After 1 week
After 4 to 6 weeks
4 to 6 weeks
After a few days
The result
A period of 3 to 4 months is ideal to appreciate the results of breast augmentation, as the breasts have regained their suppleness and the prostheses have stabilized. In a natural and realistic approach, we can affirm that the gain in breast volume has an impact on the overall silhouette and allows greater freedom of dress.