What is gynecomastia?
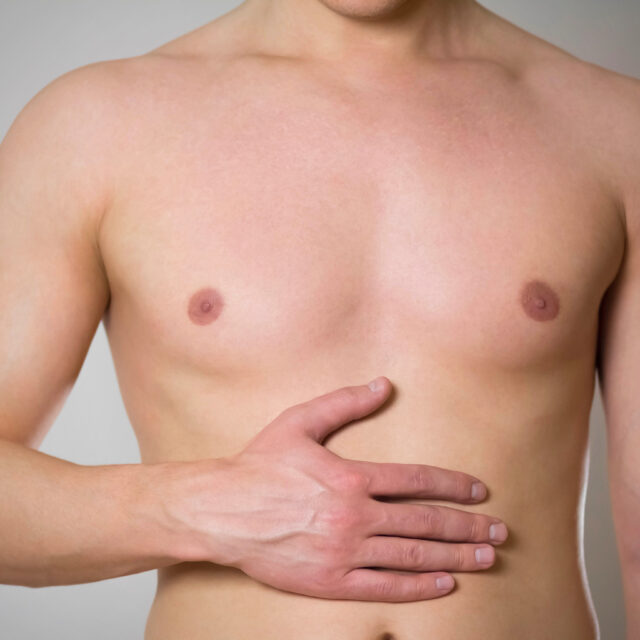
Gynecomastia refers to the abnormal and often unsightly development of the male breast. This problem can manifest itself in various forms and severities. Generally benign, gynecomastia can be resolved by a relatively simple procedure that makes the chest flatter and firmer.
Gynecomastia affects far more than just physical appearance; for many men, it can cause deep psychological distress, diminish self-esteem, and lead to social withdrawal. Professional and personalised management of gynecomastia is therefore crucial for supporting overall well-being.
Why do some men have breasts?
Gynecomastia can result from a range of factors, including hormonal fluctuations, certain medical conditions, and specific medications. Imbalances between sex hormones, particularly estrogen and androgen, can disrupt the normal function of the mammary gland, leading to its overdevelopment (hypertrophy).
Age plays a crucial role in the onset of gynecomastia. In infants, gynecomastia may develop due to the influence of maternal hormones, while in adolescents, it is often associated with hormonal changes during puberty. In older men, a reduction in androgen hormones may also be the cause. Careful medical evaluation is often required to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
What are the different forms of gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia manifests itself in different forms, each with its own characteristics and clinical implications.
Areola turgor: this minimal form of breast hypertrophy is characterised by a slight development of the mammary gland, without excess fat. Its main symptom is swelling of the nipple. Frequently observed in athletes, it is also common in adolescents.
Glandular gynecomastia: results from excessive development of the mammary gland. Clinically, the breast is firm to the touch and can sometimes be painful.
Fatty gynecomastia or adipomastia: this form is common in men who are overweight or have undergone significant weight loss. It is characterised by a soft, painless breast, as the mammary gland is not developed. Adipomastia is mainly due to excess fat.
Mixed gynecomastia: this is the most common form of breast hypertrophy in men. It combines an excess of both mammary gland and fat around the breast.
The benefits of gynecomastia surgery
- Lasting reduction of excess fat or glandular tissue
- Restoring a flat and aesthetic torso
- Techniques adapted to each type of gynecomastia
- Minimal and discreet scars
- Confidence and psychological well-being
- Fast recovery and return to work within a week
- Definitive results with low risk of recurrence
Frequently asked questions
What treatments are available for gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia can be treated in a number of ways, depending on the underlying cause and shape of the condition.
- Hormonal treatment: in some instances, gynecomastia results from a hormonal imbalance. In these cases, medical treatment aimed at restoring hormonal balance may be sufficient to reduce breast hypertrophy. This non-invasive approach can serve as an effective alternative to surgery, particularly when the imbalance is temporary.
- Plastic surgery: when gynecomastia is significant, or when other treatments have proved ineffective, plastic surgery becomes a preferred option. Two main surgical techniques are used:
- Lipoaspiration: indicated when gynecomastia is predominantly fatty. A fine cannula is inserted to aspirate excess fat, leaving a minimal scar.
- Glandular resection: this technique is preferred for treating glandular gynecomastia. It involves surgical removal of the enlarged mammary gland. The scar, although more visible, is generally well concealed.
These procedures are performed under general anesthesia and last between one and three hours, depending on the complexity of the operation. It is essential to consult a specialised plastic surgeon to determine the best therapeutic approach for each individual patient.
Is gynecomastia surgery painful?
Moderate pain may be experienced after the procedure, but is generally well managed with painkillers.
How long does it take to recover from gynecomastia surgery?
Most patients can resume their normal activities after one or two weeks, although strenuous physical activity is generally not recommended for about a month.
What are the risks associated with gynecomastia surgery?
As with any surgical procedure, there are risks such as infection, bleeding, reactions to anesthesia or unsightly scars. It’s essential to discuss the risks and benefits with your surgeon beforehand.
Are the results of surgery permanent?
Yes, the results of gynecomastia surgery are typically permanent. However, substantial weight gain, hormonal imbalances, or the use of certain medications can sometimes cause the condition to return.
How much does gynecomastia surgery cost?
The cost varies depending on the complexity of the procedure, the geographic location, and the surgeon’s expertise. It is recommended to consult a specialist for an accurate estimate that includes all additional expenses, such as anesthesia and postoperative care.
Are there any risks associated with umbilical nipple surgery?
As with any surgery, there are risks such as infection, bleeding, abnormal scarring and reactions to anesthesia. It’s essential to discuss these risks with your surgeon.
Your journey in 3 steps
- Consultation
- Surgery
- Post-operative follow-up

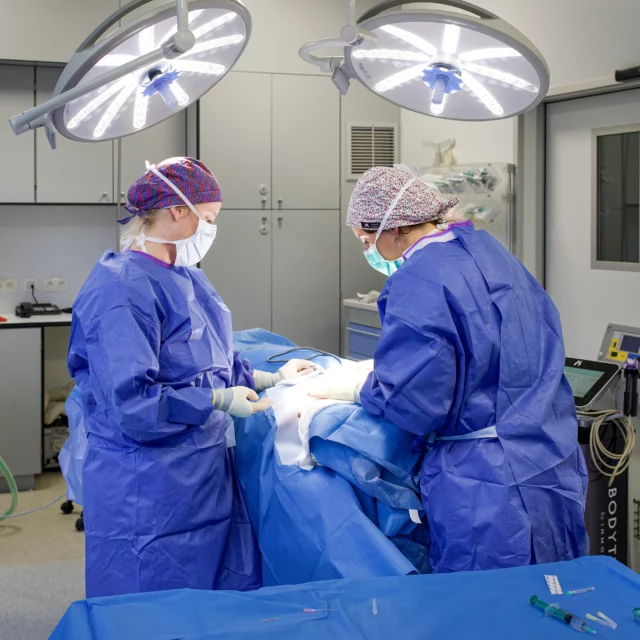
At a glance
1 to 3 hours
On an outpatient basis
After 1 day
1 to 2 weeks
1 week
1 week
After 1 week
After 4 to 6 weeks
4 to 7 days
1 day
The result
Gynecomastia surgery offers excellent, lasting and definitive results. Volumes disappear, leaving a well-shaped torso and skin stretched tight against the pectoral muscle. The development of a second gynecomastia is extremely rare, even if the gland has not been removed.
The aesthetic improvements, together with enhanced confidence and psychological well-being, make this surgery a popular choice for individuals seeking to correct gynecomastia.